Millbrook Pharmacy Health Tips
Here you will find health tips on a variety of topics. If you are looking for information that you can't find here please don't hesitate to email your suggestion/question to david@millbrookpharmacy.com.
IF YOU MISSED YOUR PILLS (ORAL COMBINATION CONTRAC

If you missed your pills (Oral combination contraceptive)
|
# of missed pills |
What to do with missed pills |
What to do with remaining pills |
Is backup contraception needed |
|
One |
Immediately |
Continue at usual time |
No |
|
Two pills on consecutive days |
Take one of the 2 pills immediately; discard 2nd missed pill |
Continue with the rest of the schedule |
Yes, for 7 days |
|
Two pills on consecutive days during day 15-21 of cycle |
Take one of the 2 pills immediately; discard 2nd missed pill |
Continue with the rest of the active pills but skip the 7 placebo pills. Re-start a new pack in place of placebo pills |
Yes, for 7 days |
LOWER BACK PAIN DRUG TREATMENT BASICS

|
Drug |
Dosage |
Comment |
|
Acetaminophen (Tylenol) |
3000 – 4000 mg total daily dose (1 or 2 XST tabs QID) |
1st line Safest of all Use around the clock instead of as needed 2 to 4 weeks duration |
|
Ibuprofen (e.g. Advil, Motrin) Anti-inflammatory agent (NSAID) |
Up to 800mg TID |
1st line May be more effective than acetaminophen Use around the clock instead of as needed 2 to 4 weeks duration Avoid if hypertension, heart failure, GI ulcers, kidney diseases |
|
Naproxen (e.g. Aleve) Anti-inflammatory agent (NSAID) |
500mg BID |
1st line May be more effective than acetaminophen Use around the clock instead of as needed 2 to 4 weeks duration Avoid if hypertension, heart failure, GI ulcers, kidney diseases |
|
Cyclobenzaprine Muscle relaxant |
5 – 10 mg TID |
2nd line High incidence of CNS side effects (e.g. sedation) Avoid in seniors (risk of falls) Limit use to 7 days only |
|
Tizanidine (e.g. Zanaflex) Muscle relaxant |
2mg starting dose TID Increase gradually, if needed, to maximum 12mg TID |
2nd line Hypotension (20% drop in blood pressure) Limit use to 7 days |
|
Methocarbamol (e.g. Robax Platinum, Robaxacet) Muscle relaxant |
1 to 2 tablets TID |
2nd line Less drowsiness than cyclobenzaprine Discolored urine (brown or green) |
|
Gabapentin (e.g. Neurontin)
|
300 – 600mg TID |
2nd line For sciatica related back pain Drowsiness & fatigue |
|
Tramadol (e.g. Zytram XL, Tramacet) or short-acting opioid (e.g. Oxycodone) |
Tramacet 1-2 tabs QID Xytram XL 150 to 400mg daily Oxycoet 1 tab q6h |
3rd line For pain not controlled by acetaminophen or NSAID No more effective than NSAID for low back pain Avoid tramadol if history of seizures or on SSRI Use only 1 to 2 weeks |
MIGRAINE DRUG TREATMENT BASICS

|
Drug |
Dosage |
Comment |
|
Acetaminophen (e.g. Tylenol) |
1000 mg every 4-6 hours (Maximum 4000mg per day) |
Mild to moderate attacks Minimal GI side effects |
|
Aspirin |
975mg – 1000mg |
Use effervescent tablets (e.g. Alka-Seltzer) for quick action |
|
Ibuprofen (e.g. Advil) |
400mg (may need repeat q4h) |
Often work quickly Use liquid gel caps for faster onset |
|
Diclofenac |
50mg (may need repeat q4h) |
Often work quickly Cambia powder for solution works even faster |
|
Naproxen (e.g. Aleve) |
500mg to 550mg |
Long-acting (12 hours) suited for prolonged migraine attacks |
|
Amerge (naratriptan) |
1 mg |
|
|
Axert (almotriptan) |
6.25mg |
Less side effects |
|
Frova (frovatriptan) |
2.5mg |
Less chance of headache return |
|
Imitrex (sumatriptan) |
50mg |
|
|
Maxalt (rizatriptan) |
5mg |
Tend to work quickly |
|
Relpax (eletriptan) |
20mg |
Tend to work quickly Less chance of headache return |
|
Zomig (zolmiriptan) |
2.5mg |
|
|
Maxalt RPD |
5mg |
Dissolves in mouth without water (convenience) Less chance of nausea Not faster onset |
|
Zomig Rapimelt |
2.5mg |
As Maxalt RPD |
|
Imitrex nasal spray |
5mg |
Faster onset than oral |
|
Zomig nasal spray |
2.5mg |
Faster onset than oral |
|
Imitrex Injection |
6mg |
Fastest onset of action |
|
Triptan + Naproxen |
500mg (naproxen) |
More effective than either alone Less recurrence of headache |
|
Migranal (dihydroergotamine) nasal spray |
1 spray (0.5mg) each nostril May repeat after 15-30 min |
An option if triptan-naproxen combo don’t work |
OPIOID RECEPTORS & THEIR ACTIONS

|
|
Mu |
Kappa |
Delta |
Nociceptin |
|
Pain relief |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
Respiratory depression |
Yes |
|||
|
Reduced GI motility |
Yes |
|||
|
Miosis |
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Euphoria |
Yes |
|||
|
Physical Dependence |
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Sedation |
Yes |
|||
|
Dysphoria |
Yes |
|||
|
Inhibition of ADH release |
Yes |
|||
|
Antidepressant |
Yes |
|||
|
Convulsion |
Yes |
|||
|
Anxiety |
Yes |
|||
|
Depression |
Yes |
|||
|
Appetite |
Yes |
|||
|
Tolerance |
Yes |
HOW DO YOU CONFIRM IF YOU'RE DIABETIC

You may have classic signs and symptoms such as tiredness, thirst, increased urination, increased hunger, blurred vision, frequent vaginal infections, and tingling or numbness in hands or feet, but the real diagnosis of diabetes is based on laboratory blood tests.
|
Blood Test |
Normal |
Diabetes |
|
FPG (Fasting Plasma Glucose) |
4-6 mmol/L |
≥ 7.0 mmol/L |
|
75 g 2hPG OGTT (Oral Glucose Tolerance Test) |
≤ 7.8 mmol/L |
≥ 11.1 mmol/L |
GERIATRIC DEPRESSION SCALE

|
Question |
Yes |
No |
|
Are you basically satisfied with your life? |
|
|
|
Are you in good spirits most of the time? |
|
|
|
Do you feel happy most of the time? |
|
|
|
Do you think it is wonderful to be alive now? |
|
|
|
Do you feel full of energy? |
|
|
|
Score 1 point for each “no” |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Have you dropped many of your activities and interests? |
|
|
|
Do you feel that your life is empty? |
|
|
|
Do you often get bored? |
|
|
|
Are you afraid that something bad is going to happen to you? |
|
|
|
Do you feel helpless? |
|
|
|
Do you prefer to stay at home, rather than going out and doing things? |
|
|
|
Do you feel that you have more problems with memory than most? |
|
|
|
Do you feel worthless the way you are now? |
|
|
|
Do you feel that your situation is hopeless? |
|
|
|
Do you think that most people are better off than you are? |
|
|
|
Score 1 point for each “yes” |
|
|
A score of 5 or greater suggests depression
METHADONE WITHDRAWAL SYMPTOMS

· Sneezing
· Eyes tearing
· Nose running
· Nausea
· Stomach cramps
· Body aches (especially joints)
· Sweating
· Dilated pupils
· Fever/chills
· Diarrhea
· Hallucination
· Insomnia
DRUGS CAUSING FALLS AMONG SENIORS

|
High risk drugs |
Moderate risk |
Low risk |
|
Antidepressants, esp. tricyclics such as amitriptyline; SSRIs are less problematic |
ACE inhibitors, esp. when combined with diuretics |
Calcium channel blockers; lower for once daily dihydropyridine such as felodipine |
|
Antipsychotics, esp. phenothiazines; risk of hypotension and Parkinson symptoms; atypicals cause less Parkinson |
Alpha blockers due to hypotension |
Nitrates; dizziness may be due to postural hypotension – advise patient to sit when using nitro spray or tablets |
|
Benzodiazepines & Hypnotics, especially long-acting type; zopiclone presents less hangover effects |
Anti-arrhythmics, e.g. digoxin and flecainide; dizziness |
Oral anti-diabetic drugs, esp. long acting sulfonylureas (e.g. chlorpropamide); dizziness from hypoglycemia |
|
Dopaminergic drugs used in Parkinson disease, e.g. levodopa causing sudden sleepiness; use lower maintenance dosage in seniors |
Anti-epileptics, e.g. carbamazepine & phenytoin; drowsiness and dizziness |
Proton pump inhibitors & H2 antagonists; dizziness, drowsiness, confusion |
|
Anticholinergics used in urinary incontinence and Parkinson disease; oxybutynin may cause acute confusion in elderly |
Antihistamines, e.g. chlorpheniramine & diphenhydramine; drowsiness |
|
|
Anti-emetics; metoclopramide associated with dizziness, drowsiness, Parkinson and movement disorders |
Beta blockers; postural hypotension & dizziness |
|
|
|
Diuretics; postural hypotension, dizziness, and nighttime urination |
|
|
|
Opiate analgesics; drowsiness and sedation; less likely with codeine |
|
HPV VACCINES GARDASIL & CERVARIX

|
|
HPV types |
Male or female |
# of doses |
Cervical, vulvar, vaginal cancers |
Anal cancer |
Ano-genital warts |
|
Gardasil |
6, 11, 16, 18 |
Both |
3 doses (0, 2, 6 month) |
Females 9 to 45 years |
Both males and females 9 – 26 years |
Females 9 – 45 years Males 9 – 26 years |
|
Cervarix |
16,18 |
Female only |
3 doses (0, 1, 6 month) |
10 to 25 years of age to prevent cervical cancer |
NA |
NA |
CANADA VIGILANCE PROGRAM

To report a suspected adverse reaction to these health products, please contact the Canada Vigilance Program of Health Canada by one of the following methods:
Telephone: 1-866-234-2345
Facsimile: 1-866-678-6789
Canada Vigilance Program
Marketed Health Products Directorate
Ottawa, Ontario, AL 0701C K1A 0K9
E-mail: CanadaVigilance@hc-sc.gc.ca
The Canada Vigilance adverse reaction reporting form, including a version that can be completed and submitted online, is located in the MedEffect area of the Health Canada Web site.
HOW TO DIFFER COLD, SINUSITIS, AND ALLERGY

|
|
Symptoms |
Onset |
Typical Duration |
|
Sinusitis |
Congestion
|
Develops
as a complication after a cold. Can also triggered by |
Can last weeks, months, or possibly years if not treated |
|
Colds |
Runny
nose with watery to thick yellow discharge |
Symptoms develop within 1 - 3 days of exposure to the cold virus |
5 - 7 days |
|
|
Congestion
|
Symptoms
begin almost immediately after exposure to |
Symptoms last as long as you are exposed to the allergen; if that allergen is present year round, symptoms may be chronic |
WHAT DO BLOOD TESTS TELL

|
Blood test |
Normal values |
Implications of abnormal values |
|
Red blood cells |
5 millions per microliter |
Anemia, bleeding, dehydration |
|
White blood cells |
4 to 10 thousands per microliter |
Infection, blood cancer, immune system disorder |
|
Platelets |
150,000 to 450,000 per microliter |
Bleeding disorder, thrombotic disorder |
|
Haemoglobin |
150g per liter |
Anemia, thalassemia, diabetes (A1c) |
|
Hematocrit |
0.4 to 0.5 |
Anemia, dehydration, blood disorder, bone marrow disorder |
|
Mean corpuscular volume |
80 – 100 fL |
Anemia, thalassemia |
|
Glucose (fasting) |
3-6 mmol/L |
Diabetes |
|
Calcium |
2-3 mmol/L |
Kidney, bone, thyroid, cancer, malnutrition |
|
Potassium |
3-5 mmol/L |
Dehydration, kidney disease, liver disease, heart failure, high blood pressure |
|
Sodium |
130-150 mmol/L |
|
|
HCO3 |
25-30 mmol/L |
|
|
Cl |
100 mmol/L |
|
|
Troponin |
<0.01ug/L |
Heart attack |
|
Creatine kinase |
<130 u/L |
Heart attack |
|
Total cholesterol |
<5 mmol/L |
Increased risk for coronary heart disease |
|
LDL |
<3 mmol/L |
|
|
HDL |
>1 mmol/L |
|
|
Triglycerides |
<2 mmol/L |
|
|
|
|
|
MISSING BIRTH CONTROL PILLS

|
|
Week 1 |
Week 2 or 3 |
Backup contraception |
Emergency contraception |
|
Miss 1 or more pills |
Take “1” immediately Continue with pack |
|
For next 7 days |
If unprotected sex in past 5 days |
|
Miss 1 or 2 pills |
|
Take “1” pill immediately Continue with pack Skip placebo pills and start new pack in placebo week |
|
|
|
Miss 3 or more pills |
|
As above |
For next 7 days |
For unprotected sex until 7 pills have been taken |
VITAMIN D TO PREVENT FALLS

Vitamin D improves muscle strength among the elderly and helps prevent falls and fractures. The daily dose must be 800 i.u. per day or more (any less won’t do). Some prescribers are giving 50,000 i.u. once a month for convenience.
Measures to reduce falls:
- Watch out for drugs that cause drowsiness, dizziness, impaired balance
- Exercise to strengthen muscles and balance
- Remove tripping hazards at home
- Correct vision with glasses or surgery
DIAPHORESIS

Excessive sweating may be caused by something as tame as exercise and spicy food but at other times, it may be a sign of emergency medical condition that requires treatment.
|
Diabetes |
Insulin & other anti-diabetic drugs may cause hypoglycemia which leads to diaphoresis |
|
Stimulants |
Caffeine, Cocaine, amphetamine |
|
Central acting drugs |
Alcohol, morphine, anti-psychotics |
|
Withdrawal from drugs |
Alcohol, narcotic pain killers |
|
Serotonin syndrome |
Excessive use of Prozac-like drugs |
|
Heart attack |
Rapid firing of sympathetic system |
|
Infections |
Accompanied by fever and chills, especially in malaria & TB |
PSYCHOSIS

A person suffering from psychosis becomes detached from reality. His thinking is disorganized, his behavior is bizarre. He is unable to carry out his daily living activities, nor is he able to interact socially. There may be hallucination and delusional thoughts.
Substances that contribute to psychosis:
|
OTC |
Prescription |
Illicit |
|
Antihistamines |
Antidepressants |
Amphetamine |
|
Dextromethorphan |
Antiepileptics |
Cocaine |
|
Phenylpropanolamine |
Benzodiazepines |
LSD |
|
|
Levo-dopa |
Marijuana |
|
|
Methylphenidate |
|
DRUGS IN VIRAL RHINITIS (COMMON COLD)

|
Drug |
Comment |
|
Decongestant (e.g. pseudoephedrine) |
Relieve nasal congestion and improve air flow Single dose gives relief for 3 to 10 hours Safe to use for 3 days |
|
1st generation antihistamines (e.g. Benadryl) |
May reduce nasal secretion but does not improve recovery time |
|
2nd generation antihistamines (e.g. Claritin) |
Non-sedating but no anticholinergic activity and no evidence to support their use alone in controlling rhinorrhea |
|
Antihistamine-Decongestant combo |
Have been shown to improve short-term nasal symptoms |
|
Vitamin C |
Daily intake of 1 g is associated with a reduction in duration & severity of symptoms |
|
Zinc lozenges |
Improved benefit (reduced symptoms & duration of the cold) when started with the onset of symptoms |
|
Echinacea purpurea |
Probably effective in the prevention and treatment of common cold in adults May reduce the severity of symptoms among children if given early |
|
North American ginseng |
Given daily starting in November for 4 months significantly reduces number, severity and duration of colds |
|
Acetaminophen or ibuprofen |
May be helpful for fever or headache in pre-school children |
|
Saline drop |
Aids in cleaning the nose in infants |
WHICH BLOOD PRESSURE PILL IS SAFE DURING PREGNANCY

|
Acceptable choices |
Comment |
|
Labetalol |
|
|
Extended-release nifedipine (e.g. Adalat-XL) |
It isn't associated with
significant adverse outcomes in newborns and infants. |
|
Methyldopa |
|
PNEUMONIA TREATMENT OPTIONS

|
Class |
Drug |
Adverse |
|
Aminoglycoside |
Gentamicin, tobramycin |
Nephrotoxicity, ototoxicity |
|
Cephalosporin (1st generation) |
Cefazolin |
Anaphylaxis, rash, kidney & liver toxicity |
|
Cephalosporin (2nd generation) |
Cefaclor, cefprozil, cefuroxime |
|
|
Cephalosporin (3rd generation) |
Cefotaxime, ceftazidime, ceftriaxone |
|
|
Cephalosporin (4th generation) |
Cefepime |
|
|
Fluoroquinolone |
Ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, moxifloxacin |
GI upset, photosensitivity, cartilage damage, headache, dizziness |
|
Glycopeptides |
Vancomycin |
Nephrotoxicity, ototoxicity, intense flushing (red man syndrome) |
|
Ketolide |
Telithromycin |
Nausea/vomiting, hepatotoxicity |
|
Lincosamide |
Clindamycin |
Diarrhea, n & v, abdo pain |
|
Macrolide |
Azithromycin, clarithromycin, erythromycin |
GI upset, jaundice |
|
Nitroimidazole |
Metronidazole |
GI upset, taste alteration, dizziness |
|
Oxazolidinone |
Linezolid |
GI upset, bone marrow suppr |
|
Pencillin |
Pen-V, Pen-G, amoxicillin, ampicillin, cloxacillin |
Allergy, GI upset, nephrotoxicity |
|
Rifamycin |
Rifampin |
Rash, liver toxicity, thrombocytopenia, body fluid discoloration (contact lens stain) |
|
Sulfonamide |
Co-trimoxazole |
GI upset, rash |
|
Tetracycline |
Doxycycline |
GI upset, photosensitivity |
TOXIC EPIDERMAL NECROLYSIS (TEN)

It is a drug reaction whereby the skin is peeling off from all over the body. Epidermal cells keratinocytes which hold the skin to the body are dying out (necrosis), hence the peeling off.
Some consider TEN to be a more severe form of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome.
There is an initial week of fever before red rash and skin peeling.
Most affected are the epithelia covering the mouth, eyes, and vagina where there are blisters, crusts, and ulceration.
Treatment is to remove the offending drug, place patient in burn unit or intensive care, and intravenous immunoglobulin.
HYPOGLYCEMIA & ADRENERGIC COUNTER REGULATION

Hypoglycemia may come about for various reasons, e.g. malnutrition, exercise, excessive dosage of antidiabetic drugs. The manifestations of hypoglycemia include: excessive hunger, chilliness, trembling, dizziness, speech disorders, sensory and/or visual disturbances, shallow respiration or bradycardia. In more severe cases, the clinical symptoms of a stroke or coma appear.
Our body responds to hypoglycemia by initiating adrenergic counter-regulation which brings about a new set of symptoms: sweating, damp skin, anxiety, tachycardia, hypertension, palpitations, angina pectoris and cardiac arrhythmias.
However, under the influence of sympatholytic drugs such as beta-blockers, clonidine, the signs of adrenergic counter-regulation to hypoglycemia may be reduced or absent.
IMMUNE GLOBULIN: HEART ATTACK & STROKE

The use of immune globulin in Canada is on the rise:
- Replacement therapy for primary or secondary immunodeficiency syndromes
- Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura
- (off label)Passive immunizing agent or immunomodulating agent
Immune globulin increases serum viscosity which may be the causative factor for stroke, heart attack, thrombosis, and pulmonary embolism. Risk factors include dehydration (e.g. exercise and use of diuretics), age, atherosclerosis.
MEDICATION INDUCED HEADACHE

This phenomenon occurs in people who use painkillers for migraine or tension headaches. When these painkillers are used at higher than recommended dosage for too long, your body becomes used to the medication. “Rebound” or “withdrawal” headache occurs when you don’t take another pill. You will experience this headache almost every day, all day, even when you wake up in the morning. You feel this steady pain all over your head.
Common medicines that cause medication headache:
- Codeine
- NSAID’s
- Acetaminophen
- Triptans
- Ergotamine
Treatment is to stop, completely, all painkillers. Be aware when you stop the painkillers, the headaches will get worse for a while. You may also feel sick, anxious and sleep badly. However, medication headache should go away in a week, although in some cases it takes weeks or months.
Sometimes, your doctor may prescribe an alternate painkiller to ease off your drug-free period, e.g. a course of NSAID or low dose amitriptyline.
To prevent medication headache:
- Do not use headache pills for 2 or more consecutive days
- Do not use headache pills for more than 15 days in a month
- Avoid codeinated products because they are more likely to cause medication headache
NEEDLE INJURY HEPATITIS B CONCERN

Sharps injuries or blood/mucous membrane exposure poses a risk of transmitting bloodborne pathogens such as hepatitis and HIV.
The exposure site should be washed immediately with soap and water, and mucous membranes should be flushed with water.
The risk of developing hepatitis from a percutaneous exposure can be as high as 1 in 3.
Vaccine responders do not require treatment.
Nonresponders with only 1 vaccination series should get one dose of hepatitis B immune globulin (HBIG) and re-vaccination.
Nonresponders who have had 2 vaccination series should get 2 does of HBIG given 1 month apart.
For unvaccinated workers, the vaccine series should be inititated. HBIG is also indicated if the source is hepatitis B positive.
NEEDLE INJURY AT WORK & HIV CONCERN

Sharps injuries or blood/mucous membrane exposure poses a risk of transmitting bloodborne pathogens such as hepatitis and HIV.
The exposure site should be washed immediately with soap and water, and mucous membranes should be flushed with water.
The average risk for HIV transmission after a percutaneous exposure to HIV-infected blood is 1 in 300. After a mucous membrane exposure, risk is 1 in 1000.
Start antiretroviral PEP (postexposure prophylaxis) as soon as possible (e.g. within hours) after exposure and continue for 4 weeks unless source is found HIV-negative.
Two-drug therapy is used if the HIV status of the source is unknown (e.g. needle from a sharps container). Examples include zidovudine/lamivudine (Combivir) and tenofovir/emtricitabine (Truvada).
Additional drugs (e.g. lopinavir/ritonavir – Kaletra) may be necessary if the exposure is severe (e.g. deep puncture) or the source has symptomatic HIV infection.
MISSED PILLS

It is not easy to be perfect taking pills. We are bound to miss a pill here and there because
our life is never simple. In a 2002 Canadian Contraceptive Study, 6 out of
10 women had missed at least 1 pill during the previous 6 months. And 1 out of
10 missed 6 pills or more. Forgetting a pill in the 2nd or 3rd
week of the 21-day cycle is not likely to increase the risk of ovulation. But
if pills are missed at the beginning or the end of the 21 day cycles, there is
much higher risk of ovulation.
|
|
Week 1 |
Week 2 |
Week 3 |
|
Missed 1 pill |
Take it as soon as remembered (may mean taking 2 pills in 1 day) |
||
|
Missed 2 or more pills in a “continuous” regimen |
· Take 2 pills as soon as possible and continue rest of package as usual. · Use a back up method of contraception for 7 days after missed pill. · Use emergency contraception after unprotected intercourse. |
||
|
Missed 2 or more pills in a “cyclic” regimen |
As above |
Discard the remainder of the pack and start a new pack on the day when remembered. Menstruation may not occur in that month. Use a back up method of contraception for 7 days after missed pills. Use emergency contraception after unprotected intercourse
|
|
COLD OR FLU

|
Symptom |
Cold |
Flu |
|
Fever |
No |
Yes |
|
Headache |
No |
Yes |
|
Aches & pain |
No |
Yes |
|
Weak/tired |
No |
Yes |
|
Runny, stuffy nose |
Yes |
No |
|
Sneeze |
Yes |
No |
|
Sore throat |
Yes |
No |
|
Complication |
Bronchitis, pneumonia |
Kidney, heart failure |
GOUT DIET
Basically, you try to avoid food that are high in protein and purine which, when metabolized, becomes uric acid - the culprit in gout.
|
Reducing |
Increasing |
|
Beef, pork, lamb |
Physical exercises |
|
Gravy (meat based) |
Control body weight |
|
Seafood (anchovies, cod, haddock, herring, sardine, mussels, scallops) |
Fresh vegetables (except those mentioned in left column) |
|
Mushrooms, legume foods like peas, beans and lentil, and vegetables such as cauliflower, spinach and asparagus. |
Fresh fruits (e.g. wild cherry, black cherry) |
|
Potato and corn (not more than twice/week) |
Water |
|
Alcoholic beverages, especially beer. |
CHLAMYDIA & GONORRHEA TREATMENT

|
|
Chlamydia |
Gonorrhea |
|
Causative organism |
C. trachomatis |
N. gonorrhoeae |
|
Incubation |
More than a week |
Less than a week |
|
Onset |
Gradual |
Sudden |
|
Dysuria |
Mild |
Severe |
|
Discharge |
Little Mucoid |
Plentiful Purulent |
|
Treatment |
|
Single dose of either
|
PROPHYLAXIS FOR DENTAL PROCEDURES

|
First choice |
Amoxicillin 2g |
|
If allergic to ampicillin (amoxicillin) |
Cephalexin 2g Or below |
|
If allergic to pencillins |
Clindamycin 600mg or Clarithromcin 500mg or Azithromycin 500mg |
The single dose is taken 30 to 60 minutes before procedure (or up to 2 hours after procedure).
HEART FAILURE SYMPTOMS
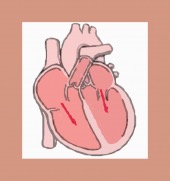
|
Common symptoms |
Atypical symptoms |
|
Dyspnea, orthopnea, exercise intolerance, fatigue, fluid retention, weight gain, nocturia, cough |
Cognitive impairment, delirium, anorexia, nausea, abdominal discomfort, oliguria, cyanosis |
Heart Failure Classes
|
Class I |
No symptoms |
|
Class II |
Symptoms with regular daily activities |
|
Class III |
Symptoms with less than regular activities |
|
Class IV |
Symptoms even at rest |
HEART FAILURE TREATMENT
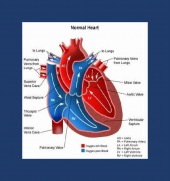
|
|
ACE inhibitor |
Beta blocker |
ARB |
Spironolactone |
Cardiovascular risk factors |
Lifestyle |
|
HF symptoms + LVEF<40% |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
Hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes to be aggressively managed |
Salt restriction, exercise |
|
If ACEI not tolerated |
|
Yes |
Yes |
|
Yes |
Yes |
|
If beta blocker not tolerated |
Yes |
|
Yes |
|
Yes |
Yes |
|
If still HF symptoms |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Yes |
Yes |
|
Severe HF + LVEF<30% |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
QUADRUPLE THERAPY FOR H.PYLORI ULCER

The American College of Gastroenterology recommends either triple or quadruple therapy as first-line for treating ulcers caused by H. pylori.
Quadruple therapy is a good first choice for patients who have recently used a macrolide or are allergic to penicillin. The course should last 10 to 14 days.
|
Losec 20mg BID |
Nexium 20mg BID (or 40mg OD) |
Pantaloc 40mg BID |
Pariet 20mg BID |
Prevacid 30mg BID |
Tetracycline 500mg QID |
Metronidazole 250mg QID or 500mg TID |
Bismuth compound BSS 525mg QID |
|
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
||||
|
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
||||
|
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
||||
|
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
||||
|
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
TRIPLE THERAPY FOR ULCERS CAUSED BY H.PYLORI

The American College of Gastroenterology recommends either triple or quadruple therapy as first-line for treating ulcers caused by H. pylori.
Triple therapy is recommended for 14 days.
|
Losec 20mg BID |
Nexium 20mg BID (or 40mg OD) |
Pantaloc 40mg BID |
Pariet 20mg BID |
Prevacid 30mg BID |
Biaxin 500mg BID |
Amoxil 1 gm BID |
Metronidazole 500mg BID |
|
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|||||
|
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|||||
|
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|||||
|
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|||||
|
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|||||
|
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|||||
|
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|||||
|
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|||||
|
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|||||
|
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
CRESTOR STARTING DOSE
|
|
5mg |
10mg |
20mg |
|
Most patients |
Yes |
||
|
Patients switched from another statin |
Yes |
||
|
Patients who do not need aggressive LDL-C reduction |
Yes |
||
|
Patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance <30ml/min) |
Yes |
||
|
Asians |
Yes |
||
|
Patients with severe hypercholesterolemia |
Yes |
Maintenance dose for most patients is 10mg daily.
Crestor may be taken with or without food, morning or evening.
30 SECOND ASTHMA TEST
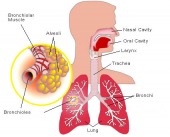
|
Criteria |
Yes |
No |
|
Does your asthma make you cough, wheeze, or tight chest 3 or more times per week |
||
|
Do you wake in middle of night due to asthmatic cough, wheezing or tight chest at least once a week |
||
|
Do you stop exercising at least once in the past 3 months |
||
|
Do you miss school or work due to asthma at least once in past 3 months |
||
|
Do you use your acute relief inhaler (fast-acting bronchodilator) more than 3 times a week (Do not include exercise dose) |
If the answer is “Yes” to any of the above 5 questions, your asthma is not under full control. And you need to see your doctor to revise the strategy.
HEART PATIENT LIFE GUIDES
To prevent another heart incident, the patient should be aggressive to follow established guidelines. BLOOD THINNERS: Aspirin 81mg daily (325mg/day if stent or bypass); add Plavix if stent/acute episode CHOLESTEROL: LDL under 2 BLOOD PRESSURE: Keep under 140/90; if diabetes/kidney disease, keep under 130/80 BLOOD PRESSURE: ACE inhibitor/Beta blocker improve outcome; may add thiazide if needed FLU SHOT: A must each year for cardiac patients PHYSICAL ACTIVITY: 30 to 60 minutes a day 5 days a week WEIGHT: Lose extra weight gradually Waistline 102cm for men, 88 for women
ADRENAL INSUFFICIENCY
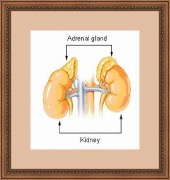
Adrenal insufficiency refers to the inability of the adrenal glands to produce a normal quantity of hormones, especially cortisol and aldosterone. The affected person has a reduced ability to cope with stress. Adrenal insufficiency is a life-threatening condition. The symptoms of adrenal insufficiency usually begin gradually but get worse when exposed to stress such as illness and accident. Characteristics of the disease are
- chronic, worsening fatigue
- muscle weakness
- loss of appetite
- weight loss
- nausea & vomiting
- diarrhea
- dehydration
- low blood pressure and fainting while standing
- loss of consciouness
- bronze color pigmentation on skin and mucous membranes
- salt loss and craving for salty food
- irritability and depression
- low blood sugar
- irregular or no menstrual periods
OPIOID ANALGESICS AND SEROTONIN TOXICITY

When a person is already on Prozac-like antidepressant, he should be careful to select a pain-killer from among the opioids. This is because some opioids (meperidine, methadone, tramadol, dextromethorphan, propoxyphene) possess serotonin reuptake inhibitor activity. Combination may raise serotonin level to toxic levels: agitation, clonus, hyper-reflexia, hyperthermia, and risk of death. Other opioids (codeine, morphine, oxycodone) don’t seem to have serotonergic property.
STRESS COUNTER

|
Life Event |
Mean Value |
Life Event |
Mean Value |
|
Death of spouse |
100 |
Trouble with in-laws |
29 |
|
Divorce |
73 |
Un-fulfiled personal goals |
28 |
|
Marital Separation |
65 |
Wife starts work or quits work |
26 |
|
Jail term |
63 |
Begin or end school |
26 |
|
Death in family |
63 |
Change in living conditions |
25 |
|
Personal injury/illness |
53 |
Revision of personal habits |
24 |
|
Marriage |
50 |
Trouble with boss |
23 |
|
Fired at work |
47 |
Change in work hours or conditions |
20 |
|
Marital reconciliation |
45 |
Change in residence |
20 |
|
Retirement |
45 |
Change in schools |
20 |
|
Health issue of family member |
44 |
Change in recreation |
19 |
|
Pregnancy |
40 |
Change in church activities |
19 |
|
Sex difficulties |
39 |
Change in social activities |
18 |
|
New family member |
39 |
Bank loan for small purchases |
17 |
|
Business readjustment |
39 |
Change in sleep habits |
16 |
|
Change in financial state |
38 |
Change in number of family get-togethers |
15 |
|
Death of a close friend |
37 |
Change in eating habits |
15 |
|
New line of work |
36 |
Vacation |
13 |
|
Arguments with spouse |
35 |
Christmas |
12 |
|
Bank loan for big purchase |
31 |
Minor violations of the law |
11 |
|
Foreclosure |
30 |
|
|
|
Change in work responsibilities |
29 |
Score up to 150: 30% chance major illness 150 – 300: 50% chance >300: 90% chance |
|
FOODS HIGH IN TYRAMINE

When you are on MAOI (monoamine oxidase inhibitor), you need to restrict foods high in tyramine. Tyramine is an amino acid found in your body (and in certain foods) that helps regulate blood pressure. High levels of tyramine can cause a marked increase in blood pressure which may lead to stroke. You need to limit consumption of foods that contain a high level of tyramine: cheese, pickled foods, chocolates, certain meat (caviar, herring, liver, smoked sausages, luncheon meat), alcoholic beverages (sherry, vermouth, red wines), certain vegetables (fava beans, Italian green beans, snow peapods, sauerkraut), soups packaged with yeast products.
NICOTINE TOLERANCE SCALE
|
0 point |
1 point |
2 points |
|
|
How soon after you wake up do you smoke your 1st cigarette? |
After 30 min |
Within 30 min |
|
|
How many cigarettes a day do you smoke? |
1 – 15 |
16 – 25 |
26 or more |
|
Nicotine content of your cigarette |
Low (<0.4mg) |
Medium (between 0.5 & 0.8mg |
High (>0.9mg) |
|
Which cigarette in your day is most satisfying? |
Any time other than 1st in morning |
1st one in the morning |
|
|
Do you smoke more during the morning than rest of day? |
No |
Yes |
|
|
Do you smoke even when sick in bed? |
No |
Yes |
|
|
How often do you inhale the smoke from your cigarette? |
Never |
Sometimes |
Always |
|
Do you find it difficult not smoking in forbidden places such as library, theatre, doctor’s office? |
No |
yes |
|
Patients with a score of 7 or greater should use the 4mg strength.
Those with a score of 6 or less may use the 2mg strength.
Attention Deficit Drugs & Hospitalization
The Ritalin family of drugs (Ritalin, Concerta, Adderall) have excellent safety profile. But still, each year, there are thousands of people (adults and children) who find themselves visiting the emergency room for treatment of overdose and side effects. A very small number actually die. These events can be prevented. As for children, keep those drugs locked away to prevent accidental poisoning. As for adults, they should be screened for cardiac problems before being prescribed. These attention deficit drugs increases heart rate and blood pressure and put the patients at risk of heart attack and stroke.
REDUCE-TO-QUIT (RTQ)

Health Canada has recently approved a new regimen Reduce-to-Quit (RTQ) which allows smokers to gradually cut down on cigarette consumption before making an abrupt quit attempt.
|
1st 4 months |
Patient is to use Nicorette Gum whenever he/she has a craving to smoke, to a maximum of 20 pieces per day. Patient is to keep the smoke-free intervals as long as possible, while he/she is allowed to succumb and smoke one now and then. Nicorette Gum should be chewed slowly over 30 minutes. One may use the “chew-chew-park” method which involves chewing the gum twice and then park it in the cheek for 1 minute; repeat cycle. |
|
End of 4 months |
There should be at least 50% reduction is number of cigarettes smoked per day |
|
At 6th month |
Patient reaches Stop-to-Quit which means he/she stops smoking altogether and Nicorette gum is used to replace cigarette |
|
At 9th month |
Patient starts to gradually decrease the dose of Nicorette Gum. Patient should not stop the Gum abruptly, or risk nicotine withdrawal and relapse. Replace the displaced Nicorette Gum with sugarless gum |
|
At 12th month |
Patient stops using Nicorette Gum |
Cocaine Addiction

It is hard to get rid of cocaine habits. Cocaine assaults the pleasure centers in our brain and produces a buzz, a rush, and euphoria. Cocaine also suppresses activity of our brain cortex making it impossible to think logically, to ignore cravings and to resist another hit. Then, there are also memory circuits created by cocaine in the brain that encourage a user to consume cocaine whenever he is exposed to sight, smell, and sound of previous usage environment (such as the sight of a crack house, or the company of friends who are users themselves). Cocaine causes a feel-good rush by increasing amounts of the brain chemical dopamine. The brain reacts by cutting back regular dopamine production, making users feel lousy between hits and setting up the cycle of addiction. There is a new drug Alertec (modafinil) that seems to negate the addictive effects of cocaine. Modafinil is a stimulant used in narcolepsy. Modafinil seems to affect chemicals that in turn regulate dopamine production, a different pathway than cocaine takes in altering normal dopamine, and thus one that might counter it. Modafinil increases the activity in the prefrontal cortex, the brain's decision-making command center and the spot that allows reasoning to override impulse or emotion. Used once a day, modafinil blocks the high induced by cocaine. Modafinil also triggers something in the brain to also improve patients' mood, energy levels and ability to concentrate — effects that might counter cocaine withdrawal.
ANTIPSYCHOTICS FOR CHRONIC PAIN

One-third of Canadians suffer from chronic pain which may be due to compromised immune function and healing. Atypical antipsychotics such as olanzapine (Zyprexa), quetiapine (Seroquel), and risperidone (Risperdal) have been used to varying success to relieve chronic pain. But to be effective, these agents require concomitant administration of other agents: acetaminophen, NSAIDs, opiates, antidepressants (fluoxetine, sertraline, trazodone), anticonvulsants (gabapentin), benzodiazepines, and muscle relaxants (cyclobenzaprine).
|
|
Olanzapine |
Quetiapine |
Risperidone |
|
Pharmacology |
Dopamine, histamine, and adrenergic receptors |
||
|
Neck pain from whiplash in car accident |
1.25mg twice a week up to 2.5mg daily at bed |
|
|
|
Rheumatoid arthritis |
2.5mg at bed |
|
|
|
Lower back from a fall |
|
|
0.25mg to 0.5mg daily |
|
Neck & back pain from spinal fusion |
|
|
0.5mg to 1.5mg |
|
Fibromyalgia |
2.5 to 20mg daily |
25 to 200mg daily |
|
|
Headache |
2.5 to 10mg daily |
|
|
|
Multiple pains (fibromyalgia, dysmenorrheal, migraine) |
Low dose |
25 to 50 mg at bed plus lamotrigine and escitalopram |
|
|
Side effects |
Drowsiness, dizziness, fatigue, weight gain |
||
Brain Health Comes From Heart Health
A recent study shows if you maintain a healthy heart, your brain will benefit as well. Risk factors that affect your heart health such as hypertension, smoking, obesity, diabetes and high cholesterol will undermine your brain functions. People with hypertension are at much greater risk of heart attack, stroke and dementia. But many Canadians with high blood pressure don't even know it because they do not necessarily feel unhealthy. The factors most consistently cited as protecting against dementia include higher education level, higher socio-economic status, emotional support, more physical exercise, moderate alcohol use, and use of vitamin supplements, specifically antioxidants such as vitamins C and E. Increased mental activity throughout life, such as learning new things and regularly doing crossword puzzles and reading newspapers, seems to help the brain remain healthy. Walking a mile a day will prevent mental decline by up to 50%.
INDICATORS OF UNDERLYING ILLNESS

|
Signs/Symptoms |
What they might mean |
|
Severe headaches |
Stroke, meningitis, aneurysm/bleeding brain, brain tumor |
|
Fever that lasts a week or more |
Hidden infections (e.g. urinary tract infection, tuberculosis), lymphomas, cancers |
|
Shortness of breath |
Bronchitis, obstructive pulmonary disease, heart problems, anxiety, panic attacks, pneumonia, blood clot in the lung, pulmonary fibrosis, pulmonary hypertension |
|
Diarrhea for more than 2 days, bloody diarrhea, black stools |
Infections of the bowel (e.g. bacteria, virus, or parasite; inflammatory bowel disease, colon cancer |
|
Weight loss (5%/month or 10%/year) |
Hyperthyroidism, depression, liver disease, cancer, malabsorption disorder |
|
Mental status changes, e.g. confused thinking, disorientation, sudden aggression, hallucination |
Head injury, stroke, low blood sugar, infection |
|
Flashes of light |
Retinal detachment |
|
Loss of vision, speech, or movement |
Imminent stroke |
|
Stomach full after little eating |
Stomach cancer, pancreatic cancer |
|
Hot, red or swollen joint |
Rheumatoid arthritis, joint infection |
2nd Antidepressant Usually Works

People who don't get well on their first antidepressant often succeed when they try another one, according to a large study done at the National Institute of Mental Health.
Five drugs were tested: Celexa, Zoloft, Wellbutrin, Effexor and Buspar. All proved similarly effective and relatively safe. Evidence also showed antidepressants should be given a 6-to-12-week chance to work and that if one doesn't help, another should be tried.
Within the same study, a group of patients were given Celexa plus either Wellbutrin or Buspar to enhance the effect of the former and one-third from this group became symptom-free within 14 weeks.
MAGNESIUM IS ESSENTIAL

|
Enzymes |
Magnesium is a cofactor in enzyme-assisted biochemical processes in our body |
|
Energy |
Magnesium is required for the body to produce and store energy. Magnesium-dependent enzyme helps activating adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the fundamental energy storage molecule of the body. Without magnesium, there is no energy and no life. |
|
Proteins |
Under the direction of magnesium, enzymes and nutrients work together to form the building blocks from food to create our body. RNA and DNA, which contain the genetic blueprints for the formation of all our body proteins, are also dependent on magnesium |
|
Nerve signals |
Magnesium and calcium work in conjunction with each other to create action potentials which pump nerve impulses to and fro the brain, directing our actions, including thought processes. |
|
Muscles |
Calcium causes contraction and Magnesium brings about relaxation. Magnesium deficiency leads to spasms, twitches, convulsion, asthmatic attacks, painful periods, and hypertension |
Tummy fat is serious killer

Tummy fat is the most unhealthy because it's linked to heart disease. The more central the fat, the more it's laid down in the arteries. By just lifting weights twice a week for an hour, women can battle the buildup of tummy fat that often takes hold with aging, a new study suggests. And they don’t even need to diet. Weight training adds muscle mass which helps a woman moves faster and burns calories more efficiently.
"I think exercise is the fountain of youth," Dr. Rita Redberg said. "If it was a pill, everyone would be taking it."
COMMON HEADACHE TRIGGERS

|
Chemicals |
Food |
Body Conditions |
Environment |
|
Alcohol, artificial sweeteners, caffeine, medications, MSG |
Aged cheese, chocolate, citrus fruits, cured meat, nuts, onion, salty-food |
Emotion, eye strain, fatigue, menstruation, physical exertion, skipped meals, stress |
Loud noises, weather changes |
ENDOCARDITIS NEW GUIDELINES
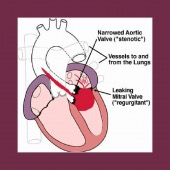
Endocarditis is an infection of the heart valves and parts of the inside lining of the heart muscle. Some patients no longer need antibiotics before dental procedures.
|
Yes to antibiotics |
No more antibiotics |
|
Artificial heart valves |
Rheumatic heart disease |
|
History of endocarditis |
Mitral valve prolapse |
|
Congenital heart conditions including incompletely repaired cyanotic congenital heart disease, 1st 6 months of repaired heart with prosthetic device, residual defect at site or nearby despite repair |
Bicuspid valve disease |
|
Heart transplant where valve defect develops |
Calcified aortic stenosis |
|
Congenital heart conditions such as ventricular septal defect, atrial septal defect, and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy |
PANCREATITIS
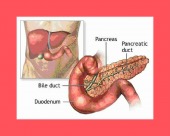
Pancreatitis is an inflammation or infection of the pancreas.
Early symptoms include nausea and abdominal pain.
Acute pancreatitis is often caused by gallstones obstructing the pancreatic duct. Digestive juices got backed up into the pancreas itself, where they attack healthy tissue and destroy cells that produce both enzymes and insulin.
Ongoing damage to enzyme-producing tissue in chronic pancreatitis leads to poor absorption (malabsorption) of nutrients, especially fats, to weight loss, and to oily, malodorous stools. And damage to or destruction of insulin-producing cells means blood sugar isn't metabolized properly, often leading to diabetes.
The other major contributor of acute pancreatitis is alcohol which causes digestive enzymes to be released sooner than normal. It also increases the permeability of the small ducts that convey enzymes within the pancreas, which allows digestive juices to leak into and damage healthy tissue. What's more, excessive alcohol intake leads to the formation of protein plugs — precursors to small stones — that block parts of the pancreatic duct.
Other factors that can cause or contribute to pancreatitis include:
- Increased blood levels of fats called trigylcerides (hyperlipidemia) or of calcium (hypercalcemia)
- Certain medications, including corticosteroids and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, blood pressure lowering drugs (thiazides), antibiotics such as tetracyclines and sulfonamides, and medications that suppress the immune system such as azathioprine and 6-mercaptopurine. Drug-induced pancreatitis constitutes 2 to 5% of reported cases acute pancreatitis. People at risk of drug-induced pancreatitis include elderlies on multiple medications, HIV patients, patients on immunomodulatory agents.
- Viral infections (e.g. mumps, hepatitis)
- Bacterial infections
DRUG INDUCED THROMBOCYTOPENIA

Thrombocytopenia is a condition where blood platelets count is less than 150,000 per cubic mm (normal range: 150,000 to 450,000). Symptoms are bruising in forearms, nose bleedings, gum bleedings, pinpoint red spots on lower legs. Severe cases involve hemorrhages, bleeding stomach and blood in stool.
Some drugs play a role in causing thrombocytopenia: quetiapine (Seroquel), olanzapine (Zyprexa), clozapine (Clozaril), pantoprazole (Pantoloc), citalopram (Celexa), clopidogrel (Plavix), heparin, valproic acid, interferon, sulfonamide antibiotics.
Although relatively rare, drug-induced thrombocytopenia may be associated with risks of morbidity and mortality.
ACCIDENTAL FALLS AMONG SENIORS

60% of trauma admissions to hospitals in Ontario are related to falls.
Falls are the most frequent cause of injury among seniors.
1 in 4 falls result in injuries including fractures and even death.
It is prudent to manage the risk factors to prevent falls:
· >65 years of age
· Inactive lifestyle
· Weakening muscle strength
· Poor balance, gait
· Improper footwear
· Orthostatic hypotension
· Use of 4 or more medications, particularly psychotropics
· Impaired cognition, memory, thinking, and judgment
· Impaired vision and hearing
· Depressive symptoms
· Incontinence
· Safety hazards in and around home and public places
WELLBUTRIN (BUPROPION) SEIZURE CONSIDERATIONS

Seizure occurrence is about 1 per 1000 in dose range of up to 300mg per day.
At 400mg dose per day, seizure occurrence increases to 4 per 1000.
Above 450mg daily dose, there is 10-fold increase in seizures.
Predisposing risk factors
· History of prior seizure
· History of head trauma
· Central nervous system tumour
· Severe hepatic impairment
· Excessive use of alcohol; addiction to opiates, cocaine, or stimulants
· Use of concomitant medications that lower seizure threshold: antipsychotics, andtidepressants, lithium, amantadine, steroids, quinolone antibiotics, anti-malarials
· Use of OTC stimulants or anorectics
· Diabetes treated with oral hypoglycemics or insulin
· Current or prior diagnosis of bulimia or anorexia nervosa
· Abrupt withdrawal from alcohol, benzodiazepines or other sedatives
GUILLAIN-BARRE SYNDROME

Guillain-Barré (ghee-yan bah-ray) syndrome is a disorder in which the body's immune system attacks our own peripheral nervous system, usually triggered by an acute infectious process. The disorder can develop over the course of hours or days, or it may take up to 3 to 4 weeks. The symptoms start in the legs which get weak and tingly. The paralysis spreads to the upper limbs and the face along with complete loss of deep tendon reflexes (knee jerks). All forms of Guillain-Barre syndrome are due to an immune response to foreign antigens (such as infectious agents or vaccines) but mistargeted to host nerve tissues instead. The end result of such autoimmune attack on the peripheral nerves is inflammation of myelin and subsequent conduction block, leading to a rapidly evolving flaccid paralysis. Frequently, the lower cranial nerves may be affected, leading to bulbar weakness (causing difficulty with eye movements, double vision), oropharyngeal dysphagia (difficulty with swallowing, drooling, and/or maintaining an open airway). In severe cases of GBS, loss of autonomic function is common, manifesting as wide fluctuations in blood pressure, orthostatic hypotension, and cardiac arrhythmias.
Prompt treatment with plasmapheresis followed by immunoglobulins and supportive care, the majority of patients will regain full functional capacity. The most critical part of the treatment for this syndrome consists of keeping the patient's body functioning during recovery of the nervous system. This can sometimes require placing the patient on a respirator, a heart monitor, or other machines that assist body function.
VITAMIN D

|
Primary Role |
Primary Benefits |
Secondary Benefits |
Deficiencies |
Overdose |
Daily Requirement |
|
|
Maintain proper blood levels of calcium & phosphate |
Healthy bone metabolism
|
Prevent some cancers
|
Rickets in children
|
Hypercalcemia
|
19-50 Years |
200 units |
|
Decrease fracture rate
|
Osteomalacia (undermineralized bones)
|
51-70 years |
400 units |
|||
|
Increase muscle strength
|
Prevent some autoimmune diseases |
Osteoporosis (porous bones) |
Calcification of kidneys, heart, lungs, & blood vessels |
>70 years |
600 units |
|
|
Reduce fall accidents |
|
|
|
|||
STRATTERA CARDIOVASCULAR CONSIDERATIONS
All medications for the treatment of ADHD are sympathomimetic. The stimulatory effects from these drugs on the sympathetic nervous system are usually mild or moderate, but in patients of all ages, particularly those with cardiovascular compromise, these effects may result in serious adverse events including sudden/cardiac death.
· STRATTERA should be used with caution in patients with hypertension, tachycardia, congenital long QT syndrome, or cardiovascular or cerebrovascular disease because it can increase blood pressure and heart rate.
· STRATTERA-treated adult subjects experienced mean increases in systolic (about 3 mm Hg) and diastolic (about 1 mm Hg) blood pressures compared with placebo.
· Sudden death has been reported in association with stimulant drugs used for ADHD treatment at usual doses in children with structural cardiac abnormalities. Although STRATTERA is not a stimulant drug, it should not generally be used in children, adolescents, or adults with known structural cardiac abnormalities.
· All drugs with sympathomimetic effects prescribed in the management of ADHD should be used with caution in patients who: a) are involved in strenuous exercise or activities, b) use stimulants, or c) have a family history of sudden/cardiac death.
· QTc prolongation was reported in two cases of intentional atomoxetine overdose which may have involved other drugs (bupropion, risperidone, quetiapine).
STRATTERA PREMISE FOR USE
Norepinephrine (along with dopamine) plays a large role in attention and focus. Our adrenal glands manufacture the hormone which is then released into the blood stream. When you increase the levels of norepinephrine in the body, you become more alert and focused. Strattera is a “selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor” which is unique in that it does not alters dopamine levels (hence less abuse potential) but does increase norepinephrine levels at nerve synapses for nerve impulses transmission. As a stress hormone, norepinephrine affects parts of the brain where attention is controlled. It initiates our survival fight-or-flight response, increasing heart rate, triggering release of glucose into blood stream, and increasing muscle readiness.
HYPOKALEMIA (LOW POTASSIUM)

Potassium is a mineral necessary for good health. It maintains water and acid balance in blood and tissue cells, and facilitates the transmission of electrical signals between cells and nerves.
Hypokalemia is a potentially fatal condition in which the blood potassium levels fall outside the normal range of 3.5 to 5.0 mEq/L. Hypokalemia is most common in people with diseases that affect kidney function, people who take diuretics, and people with eating disorders.
Early symptoms of hypokalemia, or potassium deficiency, include muscle weakness, fatigue and slow reflexes. Severe cases can result in cardiac arrest and paralysis of the lungs.
LIPID LOWERING DRUGS
|
Drug Class |
Primary Effect |
Secondary Effect |
|
Statins |
Reduce LDL |
Increase HDL Decrease TGs |
|
Ezetimibe |
Reduce LDL |
Increase HDL Decrease TGs |
|
Bile acid sequestrants |
Reduce LDL |
Increase HDL May increase TGs |
|
Niacin |
Increases HDL Lowers TGs |
Lowers LDL |
|
Fibrates |
Reduce TGs Increase HDL |
May increase LDL (in patients w high TGs) |
LIPID TARGETS & RELATED NUMBERS FOR DIABETICS
|
LDL Cholesterol |
<2 mmol/L |
|
LDL-C for those >40 years of age |
Use statin to reduce LDL 30-40% regardless of initial levels |
|
HDL-C |
1.2 mmol/L middle-age male 1.45 mmol/L middle-age woman |
|
TG |
<1.5 mmol/L |
|
TC/HDL-C ratio |
<= 4.0 |
|
A1C |
<= 7% |
|
Waist |
<102 cm for men <88 cm for women |
|
Blood pressure |
<130/80 |
|
BMI |
18 - 24 |
9 UNIVERSAL CARDIOVASCULAR RISKS

These risk factors account for 90% of all heart attacks. The two most important risk factors are cigarette smoking and an abnormal ratio of blood lipids, which together predicted two-thirds of the global risk of heart attack.
- Cigarette smoking
- Dyslipidemia
- High blood pressure
- Abdominal obesity
- Hyperglycemia
- Stress
- Lack of daily consumption of fruits and vegetables
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Lack of daily exercise
EXERCISE IS POSITIVE EXPERIENCE

- It increases heart rate and breathing rate which helps in conditioning our heart and lung functions.
- It helps us to control our body weight, diabetes, and high blood pressure.
- It increases our “High-density lipoprotein” HDL-Cholesterol which is one major factor in reducing cardiovascular diseases.
CAUSES OF HIGH CHOLESTEROL

|
Primary |
Secondary |
|
Heredity |
Diabetes |
|
Poor Diet |
Hypothyroidism |
|
Obesity |
Liver Disease |
|
Sedentary Life Style |
Chronic Renal Failure |
|
Age |
Drugs (corticosteroids, anabolic steroids, progesterone) |
|
Gender (women have lower levels) |
|
MAO INHIBITORS AND SEROTONIN REUPTAKE INHIBITORS

The 2 classes of inhibitors don’t co-exist well. If you stop one to start the other, a drug holiday is always needed. After stopping an MAO inhibitor, allow at least 2 weeks before giving any SRI. To give MAOI, stop SRI according to following table:
|
SRI |
Weeks to clear body of SRI for MAOI |
|
Venlafxaine, Nefazodone |
1 |
|
Citalopram, Escitalopram, Fluvoxamine, Paroxetine, Sertraline |
2 |
|
Fluoxetine |
5 |
TOO MUCH IRON (IRON OVERLOAD)

Undetected or untreated excess iron kills after inflicting injury to a variety of body organs, e.g. liver (cancer), (heart) attack, (brain) stroke.
Excess iron lowers the immune system. Many diseases will show a poor outcome unless any excess iron is removed: AIDs, cancer and hepatitis, for example.
Excess iron stored in the brain has been found to exacerbate severity in Alzheimer's, MS, Lou Gehrig's, Parkinson's and other diseases. Iron in the brain also leads to psychological problems.
To prevent iron overload, one should aim for “% of Saturation” (also called Transferrin Saturation TS) within 12 – 44%, and “Iron in the Blood” (i.e. Serum Ferritin SI) within 5 – 150.
DETERMINING SEROTONIN SYNDROME

There must be 4 major symptoms or 3 major plus 2 minor.
|
Major |
Minor |
|
|
MENTAL |
Confusion, Elevated Mood, Coma |
Agitation, Nervousness, Insomnia |
|
AUTONOMIC |
Fever, Hyperhidrosis |
Tachycardia, BP high or low, Dyspnea, Diarrhea |
|
NEUROLOGICAL |
Tremors, Myoclonus, Rigidity, Hyperreflexia |
Impaired Co-ordination, Akathisia, Mydriasis |
FLU VIRUS TRANSMISSION
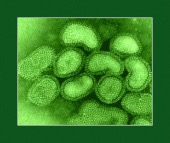
The vehicle for virus transmission is droplets from a person’s respiratory tract. One may come into direct contact, coughing/sneezing, or by hands contaminated with respiratory secretions (hence, the importance of washing hands regularly). There is an initial incubation period of 3 days then flu symptoms appear and the virus are communicable for 7 days. Children may transmit infection for longer than 7 days. If 10 (3+7) days have elapsed and no new cases of flu in your household, school, work place, or institution, one may consider outbreak to have passed.
BENEFITS OF FISH CONSUMPTION

Canada Food Guide recommends at least 2 servings (2.5 oz) of fish each week from among salmon, sardines, trout, herring and mackerel which are high in omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3 fatty acids are necessary for central nervous system development throughout fetal and infant development stages. In adults, omega-3 reduces the incidence of death due to coronary heart disease. Note: If you like tuna, select “light” tuna which come from smaller species of the fish thus carrying less mercury.
CONTIN PREPARATIONS PRIMER

Contin preparations such as Hydromorph Contin are long-acting pain formulae which are effective over a 12-hour period because of the gradual release of its active ingredient. These capsules should be swallowed whole to prevent overdose. Before you start using the pills, ask yourself: Do I have lung problems or asthma? Am I an alcoholic? Have I suffered head injury that has not healed? Am I prone to seizures? Do I have bowel problems such as constipation? Do I need to operate machinery that requires full alertness? Am I currently using medications such as MAOIs, sedatives, hypnotics, phenothiazines, antidepressants, beta-blockers, blood thinners, antihistamines, St John’s wort, OTC narcotic pain-killers? Hydromorph Contin comes in 3, 6, 12, 18, 24, & 30 mg strengths. One is not to jump strength from one level to 2 steps higher. If one has been on the drug for more than a few days, abrupt discontinuation is not recommended.
MECHANISM OF SEROTONIN SYNDROME
 (1) Increased doses of L-tryptophan will proportionally increase 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT or serotonin) formation.
(2) Amphetamines and other drugs increase the release of stored serotonin.
(3) Inhibition of serotonin metabolism by monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors will increase presynaptic 5-HT concentration. (4) Impairment of 5-HT transport into the presynaptic neuron by uptake blockers (e.g., selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressants) increases synaptic 5-HT concentration.
(5) Direct serotonin agonists can stimulate postsynaptic 5-HT receptors.
(6) Lithium increases postsynaptic receptor responses.
(1) Increased doses of L-tryptophan will proportionally increase 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT or serotonin) formation.
(2) Amphetamines and other drugs increase the release of stored serotonin.
(3) Inhibition of serotonin metabolism by monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors will increase presynaptic 5-HT concentration. (4) Impairment of 5-HT transport into the presynaptic neuron by uptake blockers (e.g., selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressants) increases synaptic 5-HT concentration.
(5) Direct serotonin agonists can stimulate postsynaptic 5-HT receptors.
(6) Lithium increases postsynaptic receptor responses.
WOMEN WORK DESKS
A woman’s work desk is usually cleaner and tidier than a man’s but it harbors 3 to 4 times more bacteria, according to a University of Arizona study by Professor Charles Gerba. The reason is women keep food in their desks. And they carry cosmetics and hand lotions with them. Makeup cases are ideal homes for germs. Phones and purses are also culprits.
SATIVEX BUCCAL SPRAY

Sativex Buccal Spray is indicated for neuropathic pain in MS patients over 18 years of age. Each spray contains delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol 27 mg/mL (from Tetranabinex—Cannabis sativa L. extract) and cannabidiol 25 mg/mL (from Nabidiolex—Cannabis sativa L. extract) in a 5.5 ml vial delivering 51 sprays. Target area is under the tongue or inside of cheek. Shake before use. The spray is refrigerated until open then at room temperature for 28 days. First day dosage is one spray every 4 hours (max 4 sprays). Adjust upward when necessary but average is 5 sprays per day. Maximum 12 sprays per day should not be exceeded. THC is a psychotropic agent which may produce physical and psychological dependence and has the potential to be abused. Relevant for pain modulation, Cannabinoid receptors are found on pain pathways in the brain and spinal cord, as well as on terminals of peripheral nervous system primary afferent neurons where they mediate cannabinoid-induced analgesia. THC can result in changes of mood, decrease in cognitive performances and memory, decrease in ability to control drives and impulses, and alteration of the perception of reality, particularly altered time sense. Fainting episodes have been observed with use of SATIVEX. Cannabinoids have cardiovascular effects that include tachycardia, and transient changes in blood pressure, including episodes of postural hypotension. Use of SATIVEX is not recommended in patients with pre-existing cardiovascular disease, such as ischaemic heart disease, arrhythmias, poorly controlled hypertension or severe heart failure.
TWINRIX FOR HEPATITIS A & B

|
Primary Schedule |
Rapid Schedule |
Anti-HAV response |
Anti-HBV response |
|
3 doses at 0, 1 & 6 months |
4 doses at 0, 7, 21 days, & 12 months
(rapid schedule for 19 & over only) |
88% at day 15 99% at day 60 100% at month 7 (100% at day 30 for rapid schedule) |
96% at day 60 100% at month 7 (82% at day 30 & 100% at 1 year for rapid schedule) |
v Protection lasts up to at least 5 years.
v A-antibodies and B-antibodies are still detected at 20 years and 15 years respectively so booster shots may not be needed during this span unless the patient is compromised in which case annual monitoring for the presence of antibodies is desirable.
v Twinrix (Adult) is for age 19 and over whereas Twinrix Junior is for 1-18 years
v Age 1-15 may use Twinrix (adult): dose 1 at 0 and dose 2 at 6 or 12 months (Total: 2 doses only).
ZYTRAM-XL

Zytram-XL is a single-entity opioid analgesic indicated for moderate pain of e.g. osteoarthritis of hip, joint, knee for several days or more (compare to Tramacet for 5 days or less). Advantage is once-daily dosing. Start with 150mg. Increase at weekly intervals to maximum 400mg. Zytram-XL must be swallowed whole. It is approved for age group 18 to 75. It must not be given if within 14 days of MAO inhibitors, or intoxication with alcohol, hypnotics, antipsychotics, opioids. Seizure can occur within normal dosage range but more so in presence of MAOI, SSRI, neuroleptics, tricyclics, opioids, head trauma, CNS infection, metabolic imbalance, alcohol/drug withdrawal, Tramadol has a potential to cause psychic and physical dependence of the morphine-type. Discontinuation should be gradual. Available in 150, 200, 300, and 400mg controlled release tablets.
CHLOROQUINE FOR MALARIA
If you plan to spend winter holidays in Jamaica or Dominican Republic, please take prophylaxis using Chloroquine. Adult Dosage: 500mg once a week 2 weeks before entering endemic area. Continue this once a week regimen during stay in endemic area and for extra 4 weeks after leaving area. Children Dosage: 8.3mg/Kg once a week for same duration as adult. If there is not enough weeks (2 weeks) before leaving Canada, double up the initial dose (e.g. adult dose will be 1000mg).
MSM (METHYLSULFONYLMETHANE)

Taking MSM orally alone or in combination with glucosamine can modestly reduce some symptoms of osteoarthritis such as pain and swelling, and improve joint function or physical function.
MSM is a naturally occurring compound found in green plants, fruits and vegetables, grains, milk. MSM is a source of sulfur for the amino acids cysteine and methionine.
MSM is primarily used for osteoarthritis. Preliminary research suggests MSM might inhibit degenerative changes in joints in animal models of osteoarthritis.
MSM is also being studied for allergic rhinitis.
Orally, MSM may cause nausea, diarrhea, bloating, headache, fatigue, insomnia, and difficulty concentrating.
For osteoarthritis, 500 mg three times daily up to 3 grams twice daily has been used.
For allergic rhinitis, 2600 mg per day has been used.
CHONDROITIN

People use chondroitin for osteoarthritis because it is endogenously found in cartilaginous tissues of most mammals and serves as a substrate for the formation of the joint matrix structure. Commercial chondroitin is made from shark and bovine cartilage.
Chondroitin protects cartilage against degradation by inhibiting the action of the enzyme leukocyte elastase, by decreasing the migration of polymorphonuclear leukocytes, and by increasing the synthesis of proteoglycans and hyaluronic acid. Chondroitin possesses antiatherogenic properties so it might protect against heart attack.
Orally, chondroitin is usually well-tolerated. Some patients can have epigastric pain and nausea.
INR: Chondroitin is a small component of a heparinoid and might have weak anticoagulant activity.
Asthma: Patients with asthma tend to have higher concentrations of chondroitin antibodies in the airway compared to people without asthma. Use chondroitin cautiously in patients with asthma.
For osteoarthritis, the typical dose of chondroitin sulfate is 200-400 mg two to three times daily or 1000-1200 mg as a single daily dose. Intermittent dosing also seems to be effective. One study has used 800 mg/day for 3 months followed by 3 months of no treatment, and then 3 months of treatment again.
Taking chondroitin sulfate along with conventional analgesics or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) is significantly more effective than analgesics or NSAIDs alone for reducing pain and improving functionality in patients with osteoarthritis of the hip and knee. Some evidence also suggests that chondroitin might allow dosage lowering or discontinuation of NSAIDs after 6-8 weeks of treatment
GLUCOSAMINE

Glucosamine is an amino sugar found in tendons, ligaments, cartilage, synovial fluid, mucous membranes, structures in the eye, blood vessels, and heart valves.
Glucosamine stops or slows the progression of osteoarthritis probably by inhibiting protein N-glycosylation and cytokine-stimulated production of mediators of inflammation and cartilage degradation. Taking glucosamine significantly improves symptoms of pain (~40%) and functionality (~40%) in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee in studies lasting up to 3 years Glucosamine will help the hip and spine as well. Glucosamine may not work well in severe osteoarthritis, especially in older and heavier patients.
For osteoarthritis, the typical dose is 1500 mg once daily or in 3 divided doses. For temporomandibular joint (TMJ) osteoarthritis, 500 mg 3 times daily has been used. Glucosamine at 1500mg daily is comparable in efficacy to 1200mg daily ibuprofen or 3000mg acetaminophen.
Side effects: Nausea, heartburn, diarrhea, drowsiness.
Diabetes: Clinical research in people with type 2 diabetes suggests glucosamine doesn't affect blood glucose or lipid levels in 3 years.
Asthmas: Glucosamine might exacerbate asthma by an unidentified allergic mechanism. Use cautiously in patients with asthma.
INR: High-dose glucosamine (3000 mg per day), combined with high-dose chondroitin sulfate (2400 mg per day) may increase INR and bleeding in patients on warfarin
BLOOD CLOTTING AMONG EVRA USERS

Evra Contraceptive Patch is a convenient form of contraception. The user applies the patch once a week for 3 weeks and off 1 week. But recent study shows Evra causes more venous thromboembolism among users when compared with oral contraceptives. It is recommended that obese women not be prescribed Evra. Other risk factors include smoking, fever, sauna/hot tub, prolonged immobility (e.g. on a plane), trauma to the body.
SORE THROAT

Don’t rush to use antibiotic when you have sore throat (pharyngitis). Most sore throats are of viral etiology. Only about 15% to 30% of cases in children and up to 10% of cases in adults are true strep throat. Viral sore throat is accompanied by cough, runny nose, or diarrhea. Symptomatic management of non-strep sore throats include acetaminophen or ibuprofen, gargle with warm salt water or ice water; throat lozenges, hard candy or ice. Runny nose can be controlled by antihistamine. Symptoms of strep throat include sudden onset of sore throat, tonsillitis with pus, swollen neck/glands, history of fever, and NO cough, runny nose, or diarrhea.
BENZOS IN ANXIETY DISORDERS

Benzodiazepines such as clonazepam and lorazepam have been well-studied for use in anxiety. They were first line agents at one time but with the advent of SSRIs (Prozac, Paxil, Effexor, etc), they are now used short-term for acute anxiety symptoms. Benzos provide rapid relief but can cause sedation, memory impairment, and dependence.
GRAVOL ABUSE
While Gravol (dimenhydrinate) is safe and effective in controlling nausea and vomiting, some people have abused it in high doses for its euphoric and hallucinogenic effects, often in conjunction with other psychoactive substances and alcohol. Gravol in high doses can cause toxic effects: ataxia, toxic psychosis, excitement, seizures, hypotension, and cardiac arrhythmias. Fatalities have resulted from the ingestion of very high doses, especially when combined with alcohol or other substances of abuse. Psychiatric symptoms which may be produced by chronic abuse include thought disorders, difficulty in concentrating, amnesia, lethargy, psychosis, hallucination, and delirium.
CHOLESTEROL GUIDELINES

Canadian Cardiovascular Society has new guidelines re cholesterol. • Screening should start for men 40 and over and women who are 50 or older or postmenopausal. For people with diabetes, smoking, hypertension, screening should be done at any age point. • For high-risk patients, aim for LDL-C of less than 2 mmol/L and the ratio of Total Cholesterol to HDL-C be less than 4. • Statin alone is usually adequate for lowering LDL-C. May add Ezetrol, cholestyramine, niacin to achieve additional goals. Fibrates are used only if niacin is ineffective because of potential muscle toxicity and renal failure from fibrates. • All patients should stop smoking, eat sensibly, lose weight, and exercise.
DREAM Study

It is not about dreams. DREAM stands for Diabetes Reduction Assessment Medication. Two drugs were tested: Altace (ramipril) and Avandia (rosiglitazone). Both drugs lowered blood sugar. But Altace did not prevent people with heart problems from developing diabetes. Avandia did delay the onset of diabetes in high risk patients on a dosage of 8mg a day for 3 years. However, Avandia brought on weight gain and edema which increased heart failure. Lifestyle changes (diet and exercise) are still best to prevent or delay diabetes.
ONTARIO BREAST SCREENING PROGRAM

Breast cancer is the most common form of cancer in women. Regular screening in women age 50 – 69 can reduce deaths by at least 30%. The Ontario Breast Screening Program permits women 50 and over get free screening without doctor referral. Test results are sent back directly to the patient and not to the doctor. Please call 1-800-668-9304 for appointment.
HOW SUSCEPTIBLE ARE YOU TO SUBSTANCE ABUSE

GENETICS: Genes passed onto you control your attraction to substances AVAILABILITY: If the substance is freely available in your neighborhood or your friendly circles, you are more likely to try it. CONCURRENT MENTAL HEALTH PROBLEMS: mood disorders, post-traumatic syndrome, anxiety disorders, personality disorders ALIENATION: loss of hope, feeling there is nothing to lose UNSTABLE LIFE: unemployment, poverty, family dysfunction.
PROSTATE "DOCTOR" IN YOUR OWN HOME
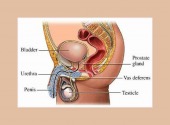
There is a new interactive tool at Prostate Cancer Research Foundation of Canada’s website (http://www.prostatecancer.ca) where a person will enter his personal stats and the system (the virtual doctor) will issue a diagnosis, disease progress report, and options available. This will tremendously reduce the guesswork that an anxious person may go through after reading/hearing all kinds of stories about the ailment. 20,000 new cases of prostate cancer are diagnosed in Canada each year and 20% of those will die annually.
STOP RECURRENT COLD SORES
It is estimated that 80% of our population harbors cold sore virus which are normally dormant and inactive. There are triggers that “wake” them up to replicate and cause uncomfortable symptoms. Avoid them if possible. • Windburn • Ultraviolet radiation (sunshine, tanning booths) • Chilling • Excitement • Emotional stress • Drying of the lips • Allergic reactions, including reactions to food • Any physical injury • Dental treatment • Fever • Menstruation • Upset stomach or GI disturbance • Minor infections (bacterial or viral e.g. cold, flu) • Any disease that increases metabolism (e.g., diabetes, hyperthyroidism) • Fatigue
NARCOTIC GROUP OPTIONS

If patient is allergic to one narcotic (rash, severe hypotension, bronchospasm, angioedema), he may be switched to another of 3 narcotic groups, or simply, avoiding risks, to be put on acetaminophen or NSAID. 1. MORPHINE GROUP: Morphine, codeine, hydrocodone, oxycodone, oxymorphone, hydromorphone, nalbuphine, butorphanol, levorphanol, pentazocine 2. PHENYLPIPERIDINES: Meperidine, fentanyl 3. DIPHENYLHEPTANES: Propoxyphene, methadone
DIABETIC PAIN

If a diabetic person suffers numbing, tingling pain in arms, hands, legs, and feet, he most likely is suffering from Peripheral Neuropathy. Recovery is slow. Sometimes, it progresses to muscular atrophy. Pain relief may come from a variety of drugs: Tricyclics (e.g. amitriptyline), Venlafaxine (Effexor-XR), Gabapentin (Neurontin), Pregabalin (Lyrica), Opioids (e.g. OxyContin).
GARDASIL FOR GENITAL WART
Genital wart is not nice. Neither is Cervical Cancer nor Vaginal Cancer. Now a vaccine is available to prevent these diseases. Gardasil vaccine is intended for girls and women 9 to 26 years of age for the prevention in cases where HPV types 6, 11, 16, and 18 are involved. It does not work in patients already afflicted with the ailments. Gardasil comes in 0.5ml single-dose vials as well as pre-filled syringe (refrigeration required). Administration is intramuscular. Three doses are required: 0, 2, and 6 months. Protection is for at least 5 years. It is not known if booster dose is required. There are no known drug interactions. Adverse effects include injection site reactions and fever.
DRUG USE ON A HOT DAY

Under hot weather conditions, patients on any class of drugs with anticholinergic properties should avoid heavy physical activities and sun exposure, and stay hydrated to stave off heat stroke. These drugs inhibit perspiration and increase body temperature. Here is the list: Prozac, Zoloft, Paxil, Luvox, Amitriptyline, Doxepin, Stemetil, Haloperidol, Risperdal, Zyprexa, Fluanxol, Lithium, Cogentin, Selegiline, Amantadine, Flavoxate, Oxybutynin, Tolterodine, Benadryl, Gravol.
OSTEONECROSIS FROM BISPHOSPHONATES

In osteonecrosis, bones are dying from lack of blood supply. Osteonecrosis can affect any bone in the body. The most common sites are the Hips, Knees, Shoulders and Ankles. Bisphosphonate therapy (mostly intravenous as in cancer-induced hypercalcemia) has been associated with osteonecrosis, primarily of the jaw. This has been observed mostly in cancer patients, but also in patients with postmenopausal osteoporosis. Risk factors include a diagnosis of cancer, chemotherapy, radiotherapy or corticosteroids; anemia, infection or pre-existing dental disease. Symptoms included nonhealing extraction socket or an exposed jawbone. Good dental hygiene can decrease the risk of osteonecrosis whereas stopping bisphosphonate therapy does not.
NAUSEA & VOMITING FROM OPIOID PAIN-KILLERS

There are 3 main causes: 1. Activation of chemoreceptor trigger zone 2. Delayed gastric emptying 3. Constipation. Solutions, in order as above, are: 1. Stemetil, Gravol which deactivate chemoreceptor trigger zone 2. Metoclopramide: a pro-kinetic agent 3. Senokot (stimulant laxative); docusate (stool softener)
IMPROPER USE OF OXYCONTIN

User of Oxycontin may or may not knowingly use it in a wrong way. There are dire consequences if the wrong way is adopted. If the tablets are crushed or chewed, the active ingredient is released immediately leading to an overdose. If the tablets are made into a solution and injected, excipients from the tablets will cause local tissue necrosis, infection, pulmonary granulomas, endocarditis, and heart-valve injury. Combining alcohol, CNS depressants and Oxycontin will lead to respiratory suppression, hypotension, severe sedation, and coma.
AFTER 1ST STROKE

To prevent a second stroke, one must get pro-active, doing things even when you are not. It is like getting groceries before you are hungry. One target is reduction of blood pressure by 10 mmHg systolic and 5 mmHg diastolic, even when you are not hypertensive. Use a diuretic (or combination of diuretic and ACE inhibitor). The other target is to lower cholesterol even in absence of heart disease. Use a statin such as Atorvastatin 80mg daily.
DEPRESSANT EFFECTS OF OPIOIDS

Opioid analgesics like oxycodone possess depressant activities like respiratory depression, blood pressure reduction, and sedation. Co-administration with other depressants such as alcohol, pain killers, anesthetics, sedatives, hypnotics, barbiturates, phenothiazines, chloral hydrate and glutethimide, MAO inhibitors (including procarbazine HCl), pyrazolidone antihistamines, beta-blockers, will only compound the problem. Respiratory depression, hypotension and profound sedation or coma may result
ASCENSIA CONTOUR GLUCOSE METER
FOR PRIMER PURPOSE Test strips: Microfill Lancing device: Microlet (Use Vaculance if alternate sites) Batteries: 2x CR2032 Coding: No need On/off button: No need>>Insert test strip and meter turns on itself Application: Touch blood drop with strip tip until meter beeps M button: Turns machine on/off; programming mode; memory button Arrow button: Changes settings; scroll through readings
DYSPHAGIA AFTER STROKE

Up to two-third of stroke patients suffer from dysphagia: Difficulty in swallowing. Dysphagia may lead to suffocation, aspiration pneumonia, dehydration, malnutrition and weight loss. Many medications compound the problem by causing mucosal ulceration (NSAIDs, Potassium chloride, Vitamin C), dry mouth (antihistamines, antidepressants), extrapyramidal symptoms (metoclopramide, antipsychotics). When taking medications, stroke patients should stay upright for 15-30 minutes after swallowing. Place medication on the more functional side of the mouth before swallowing, reduce the total number of drugs and number of each kind of pill at any one time, use medication that can be crushed and mixed with apple sauce or other thickened fluids.
SEDATION FROM NARCOTIC PAIN KILLERS

Opioid pain killers such as morphine and oxycodone may cause varying degrees of sedation among users but this sedation should subside within 5 days. For any persistence of symptoms, one should look at concurrent use of other sedating medications such as benzodiazepines, deteriorating liver or kidney functions, hypercalcemia, and respiratory failure.
